|
|
|
贝尔曼福特算法是求解单元最短路径问题的一种算法,由理查德贝尔曼和莱斯特福特创立的。有时候这种算法也被称为Moore-Bellman-ford算法,因为Edward F . Moore也为这个算法的发展做出了贡献。
它的原理是对图进行|V|-1次松弛操作,得到所有可能的最短路径。其优于迪克斯彻算法的方面是边的权值可以为负数、实现简单,缺点是时间复杂度过高,高达O(|V||E|)。但算法可以进行若干种优化,提高了效率。 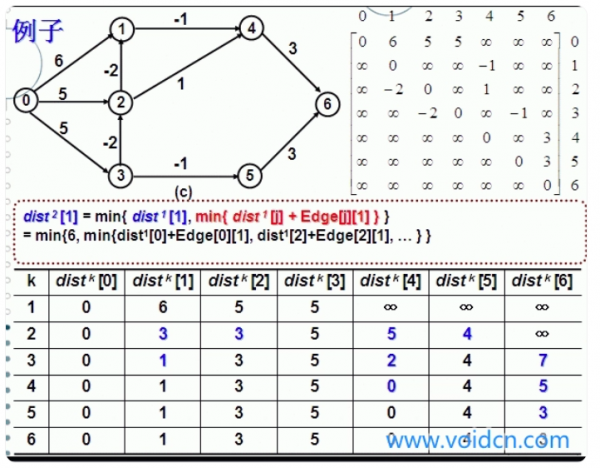
贝尔曼福特算法,分别用C语言,C++,java,python编写出来
下面是贝尔曼福特算法(Bellman-Ford Algorithm)的不同语言实现示例:
1. C语言:
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <limits.h>
- struct Edge {
- int src, dest, weight;
- };
- struct Graph {
- int V, E;
- struct Edge* edge;
- };
- struct Graph* createGraph(int V, int E) {
- struct Graph* graph = (struct Graph*)malloc(sizeof(struct Graph));
- graph->V = V;
- graph->E = E;
- graph->edge = (struct Edge*)malloc(E * sizeof(struct Edge));
- return graph;
- }
- void BellmanFord(struct Graph* graph, int src) {
- int V = graph->V;
- int E = graph->E;
- int dist[V];
- for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
- dist[i] = INT_MAX;
- dist[src] = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i <= V - 1; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < E; j++) {
- int u = graph->edge[j].src;
- int v = graph->edge[j].dest;
- int weight = graph->edge[j].weight;
- if (dist[u] != INT_MAX && dist[u] + weight < dist[v])
- dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
- }
- }
- for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
- int u = graph->edge[i].src;
- int v = graph->edge[i].dest;
- int weight = graph->edge[i].weight;
- if (dist[u] != INT_MAX && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) {
- printf("Graph contains negative weight cycle\n");
- return;
- }
- }
- printf("Vertex\tDistance from Source\n");
- for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
- printf("%d\t%d\n", i, dist[i]);
- }
int V = 5; // Number of vertices
int E = 8; // Number of edges
struct Graph* graph = createGraph(V, E);
// Add edges
graph->edge[0].src = 0;
graph->edge[0].dest = 1;
graph->edge[0].weight = -1;
// Add other edges...
int src = 0; // Source vertex
BellmanFord(graph, src);
return 0;
}
2. C++:
- #include <iostream>
- #include <climits>
- #include <vector>
- struct Edge {
- int src, dest, weight;
- };
- struct Graph {
- int V, E;
- std::vector<Edge> edges;
- };
- void BellmanFord(Graph graph, int src) {
- int V = graph.V;
- int E = graph.E;
- std::vector<int> dist(V, INT_MAX);
- dist[src] = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i <= V - 1; i++) {
- for (int j = 0; j < E; j++) {
- int u = graph.edges[j].src;
- int v = graph.edges[j].dest;
- int weight = graph.edges[j].weight;
- if (dist[u] != INT_MAX && dist[u] + weight < dist[v])
- dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
- }
- }
- for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
- int u = graph.edges[i].src;
- int v = graph.edges[i].dest;
- int weight = graph.edges[i].weight;
- if (dist[u] != INT_MAX && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) {
- std::cout << "Graph contains negative weight cycle\n";
- return;
- }
- }
- std::cout << "Vertex\tDistance from Source\n";
- for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
- std::cout << i << "\t" << dist[i] << "\n";
- }
int V = 5; // Number of vertices
int E = 8; // Number of edges
Graph graph;
graph.V = V;
graph.E = E;
// Add edges
graph.edges.push_back({0, 1, -1});
// Add other edges...
int src = 0; // Source vertex
BellmanFord(graph, src);
return 0;
}
3. Java:
- import java.util.Arrays;
- class Edge {
- int src, dest, weight;
- Edge() {
- src = dest = weight = 0;
- }
- }
- class Graph {
- int V, E;
- Edge[] edges;
- Graph(int V, int E) {
- this.V = V;
- this.E = E;
- edges = new Edge[E];
- for (int i = 0; i < E; i++)
- edges[i] = new Edge();
- }
- }
- class BellmanFord {
- void BellmanFord(Graph graph, int src) {
- int V = graph.V, E = graph.E;
- int[] dist = new int[V];
- Arrays.fill(dist, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
- dist[src] = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i < V; ++i) {
- for (int j = 0; j < E; ++j) {
- int u = graph.edges[j].src;
- int v = graph.edges[j].dest;
- int weight = graph.edges[j].weight;
- if (dist[u] != Integer.MAX_VALUE && dist[u] + weight < dist[v])
- dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
- }
- }
- for (int j = 0; j < E; ++j) {
- int u = graph.edges[j].src;
- int v = graph.edges[j].dest;
- int weight = graph.edges[j].weight;
- if (dist[u] != Integer.MAX_VALUE && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) {
- System.out.println("Graph contains negative weight cycle");
- return;
- }
- }
- System.out.println("Vertex\tDistance from Source");
- for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
- System.out.println(i + "\t" + dist[i]);
- }
-
- }
int V = 5; // Number of vertices
int E = 8; // Number of edges
Graph graph = new Graph(V, E);
// Add edges
graph.edges[0].src = 0;
graph.edges[0].dest = 1;
graph.edges[0].weight = -1;
// Add other edges...
int src = 0; // Source vertex
BellmanFord bellmanFord = new BellmanFord();
bellmanFord.BellmanFord(graph, src);
}
4. Python:
- class Edge:
- def __init__(self, src, dest, weight):
- self.src = src
- self.dest = dest
- self.weight = weight
- class Graph:
- def __init__(self, V, E):
- self.V = V
- self.E = E
- self.edges = []
- def BellmanFord(graph, src):
- V = graph.V
- E = graph.E
- dist = [float('inf')] * V
- dist[src] = 0
- for _ in range(V - 1):
- for i in range(E):
- u = graph.edges[i].src
- v = graph.edges[i].dest
- weight = graph.edges[i].weight
- if dist[u] != float('inf') and dist[u] + weight < dist[v]:
- dist[v] = dist[u] + weight
- for i in range(E):
- u = graph.edges[i].src
- v = graph.edges[i].dest
- weight = graph.edges[i].weight
- if dist[u] != float('inf') and dist[u] + weight < dist[v]:
- print("Graph contains negative weight cycle")
- return
- print("Vertex\tDistance from Source")
- for i in range(V):
- print(i, "\t", dist[i])
- V = 5 # Number of vertices
- E = 8 # Number of edges
graph = Graph(V, E)
# Add edges
graph.edges.append(Edge(0, 1, -1))
# Add other edges...
src = 0 # Source vertex
BellmanFord(graph, src)
这些示例展示了使用不同编程语言实现贝尔曼福特算法的方式。根据您选择的编程语言,使用相应的示例来实现贝尔曼福特算法。

扫码关注微信公众号,免费查看完整算法内容。[size=0.83em]设为封面
|
|
|
|
|